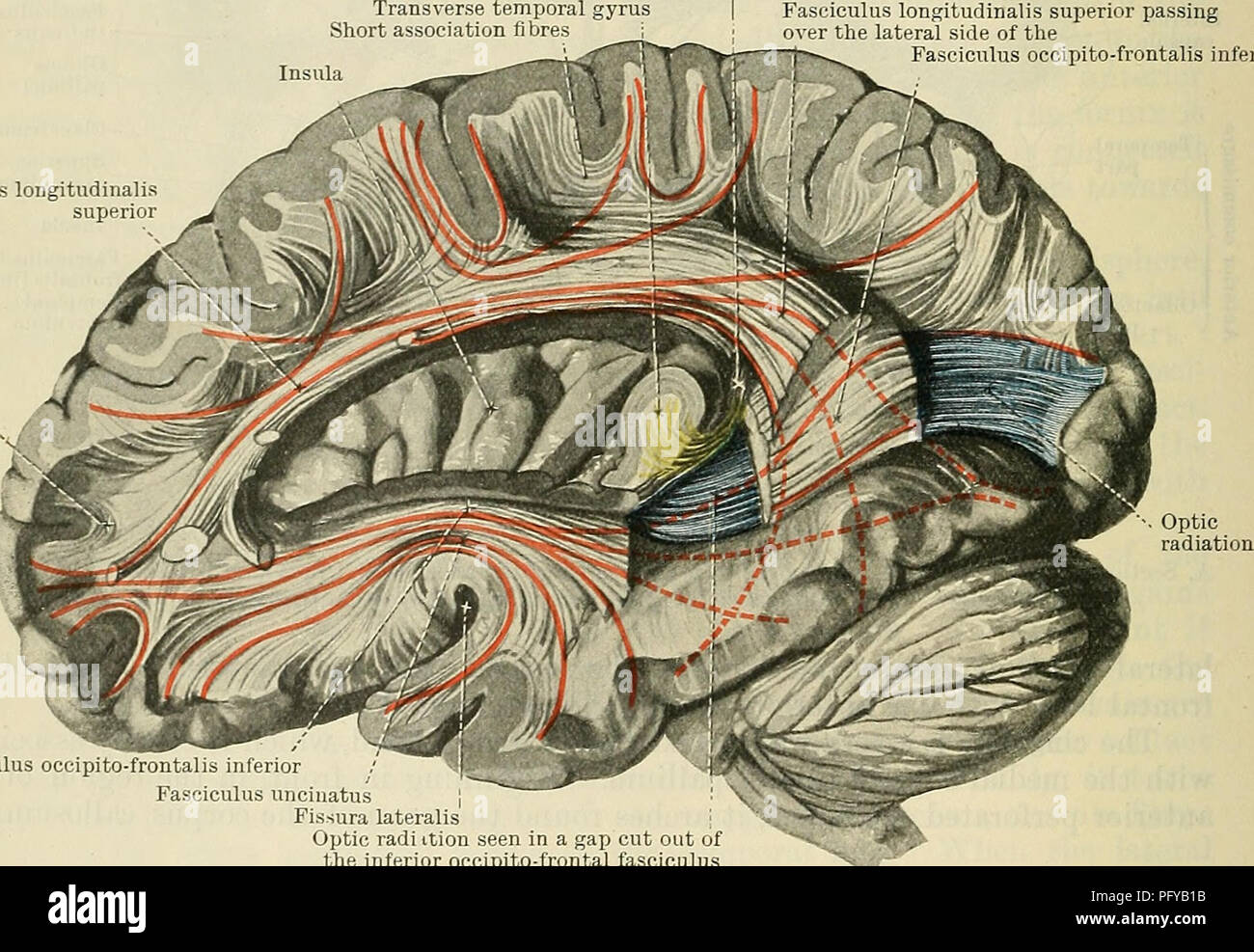
In the medulla oblongata, the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei.
They receive afferents from the corticospinal tract.
They in turn project efferents into the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle as:
- the anterior internal arcuate fibers which pass along the midline before decussating near the rhomboid fossa (floor of fourth ventricle) then passing laterally as the medullary striae;
- the anterior external arcuate fibers.
Function
Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate.
Additional images
External links
- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/frames/nlBSs/nl31fr.htm
- PubMed article
References